You may have heard that some e-bikes feature regenerative braking—technology that allows the bike to recover energy while slowing down. But is it really effective, or just a gimmick?
🚴 What Is Regenerative Braking?
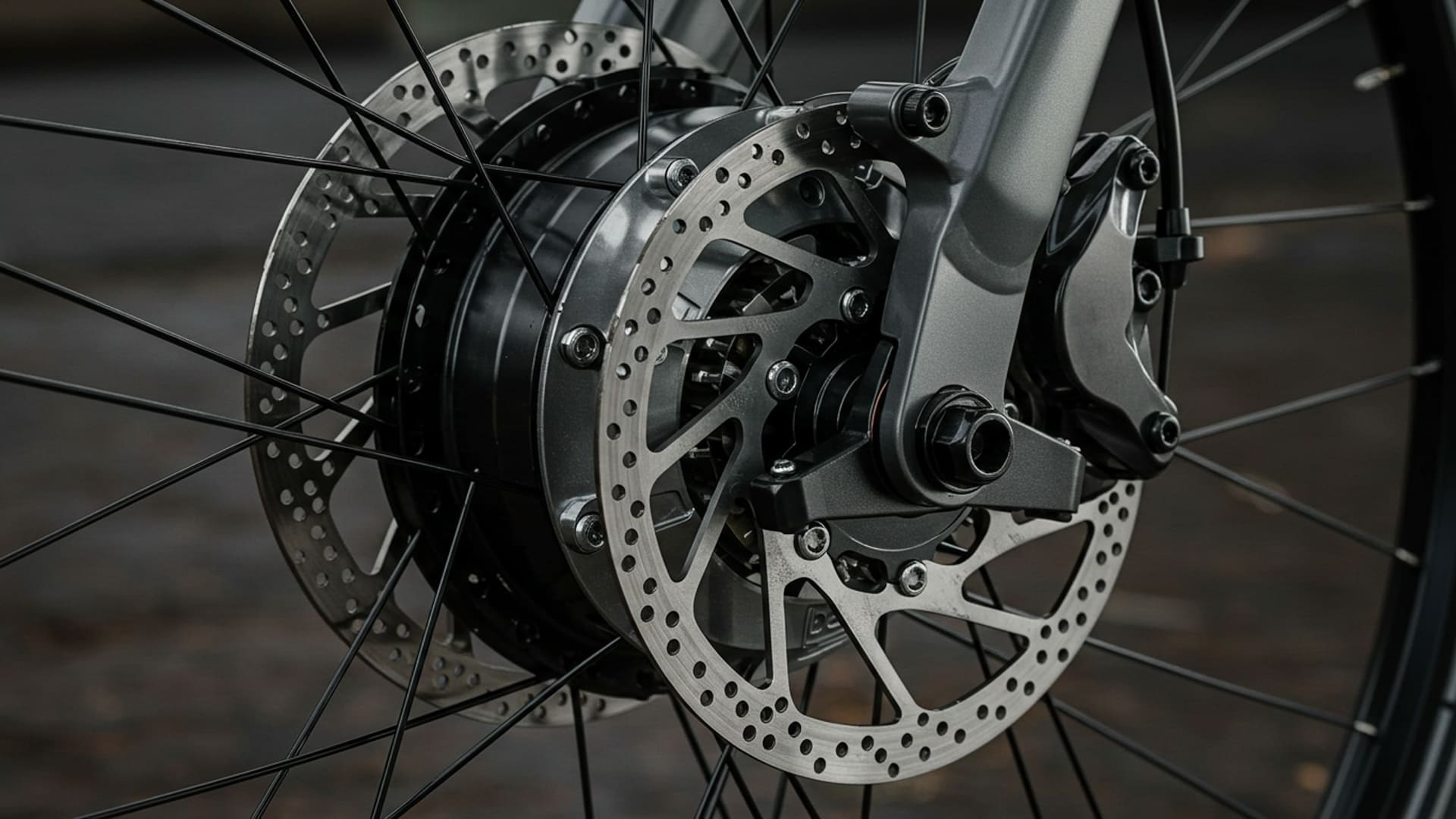
Regenerative braking allows your e-bike to capture kinetic energy during braking and convert it back into stored battery power. This system is most commonly found on hub motor e-bikes, particularly direct-drive hub motors, which have no moving gears and can reverse polarity to generate electricity.
🔋 How Much Energy Does It Save?
Here’s the truth: most e-bike regenerative braking systems recover about 5–10% of battery power at best. While this may extend your range slightly, it’s not going to double your ride distance.
Regenerative braking is most effective when:
- You ride downhill frequently
- You stop and start often (urban environments)
- Your e-bike is equipped with a direct-drive hub motor (not common on most models)
✅ Pros of Regenerative Braking
- Slightly increases battery range
- Reduces wear on mechanical brakes
- Feels smoother in stop-and-go riding
❌ Cons of Regenerative Braking
- Limited real-world battery recovery
- Only available on certain motor types
- Adds complexity and cost
- Can make pedaling less efficient due to motor resistance
🚲 Do You Need It?
For most casual riders and commuters, regenerative braking isn’t necessary. If you ride in hilly areas or value maximum efficiency, it may be worth it—but it shouldn’t be a dealbreaker.
Brands like Stealth Electric Bikes and Ariel Rider have experimented with regenerative braking, but it’s still rare in mainstream commuter models.
Final Thoughts
Regenerative braking is a cool feature—but not a critical one. If it’s included in your e-bike, great! But don’t expect it to make a major difference in your range or riding experience.







Leave a Reply